HOW TO CREATE AN AUTONOMOUS DATABASE IN OCI ?
Autonomous Database.
Prerequisite steps:
- Log in to Oracle Cloud.
- Go to the Oracle Cloud website and log in with credentials.
- Navigate to the Oracle Autonomous Database Page.
- Click on the “Navigation” menu (three horizontal lines in the top left corner) and select “Autonomous Database” from the drop-down list.
- Click on “Create Autonomous Database” On the Autonomous Database page, click on the “Create Autonomous Database” button.
1. Compartment.
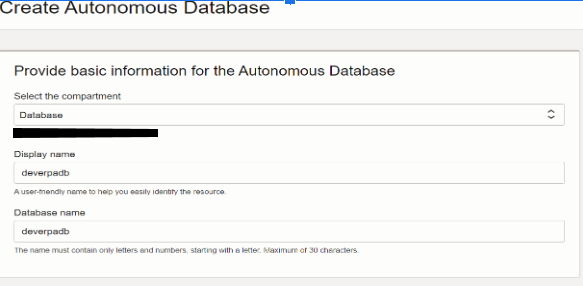
Select the compartment type as Database and display the name deverpadb and the database name deverpadb.
The below screenshot shows the basic information for the autonomous database.
2. Workload type.
We are selecting the workload type as Transaction processing.
The below screenshot shows the workload type.

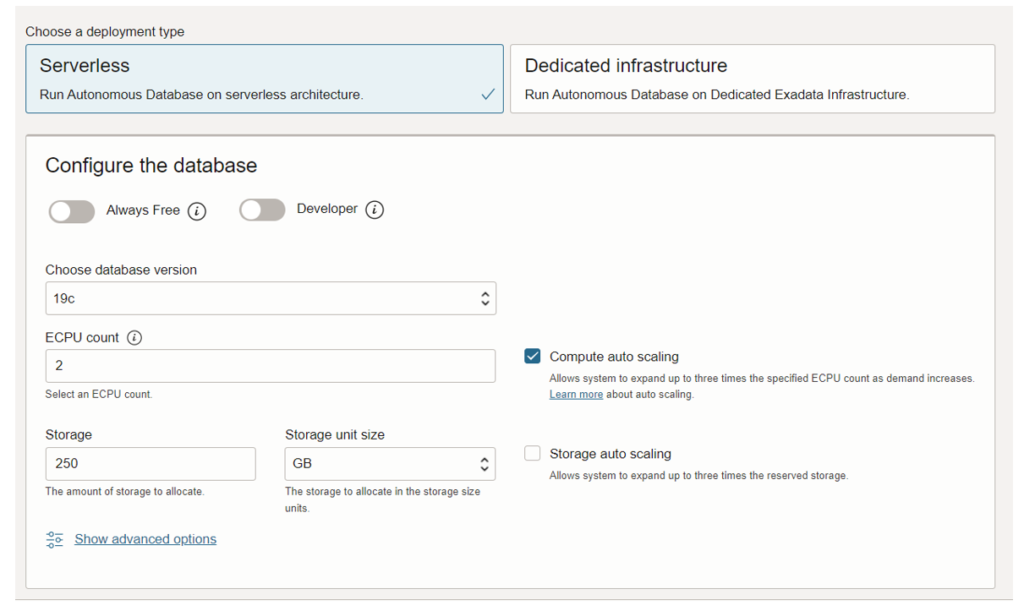
3. Deployment type and configure the database.
The deployment type is selected as serverless, and the data version ECPU count, and storage are selected as per the requirement for storage unit size in GB. By choosing to compute auto scaling database automatically uses the resources without any manual intervention.
The below screenshot shows the deployment type and configures the database.
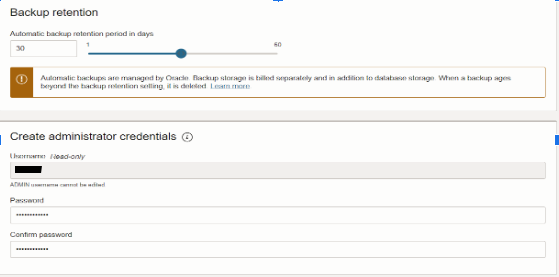
4. Back up retention and create ADMIN credentials.
Change the backup retention period for automatic backups on the Autonomous Database to a retention period between 1 day and 60 days. Set a strong ADMIN password for the database. This will be the password for the default database administrator.
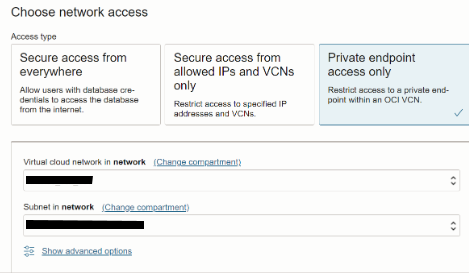
5. Network Access.
Network access type selected as Private endpoint access only. This option assigns a private endpoint, private IP, and hostname to the database. Specifying this option allows traffic only from the VCN specified; access to the database from all public IPs or VCNs is blocked. This allows us to define security rules, ingress/egress, at the Network Security Group (NSG) level and to control traffic to our Autonomous Database.
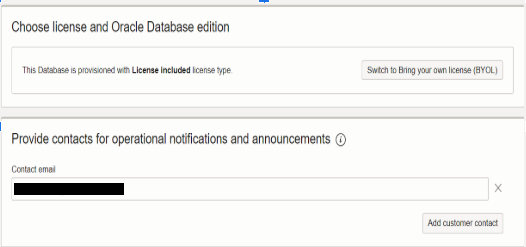
6. License and Oracle database edition then providing contact EMAIL.
License selected as License Included. Enter the contact email.
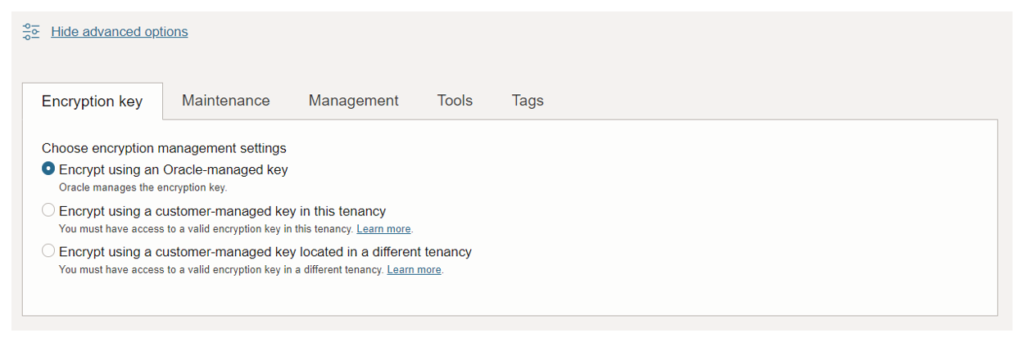
7. Encryption key.
The encryption key is selected as Oracle-Managed Master Encryption Keys on Autonomous Database Using Oracle-managed keys, Autonomous Database creates and manages the encryption keys that protect our data, and Oracle handles the rotation of the TDE master key.
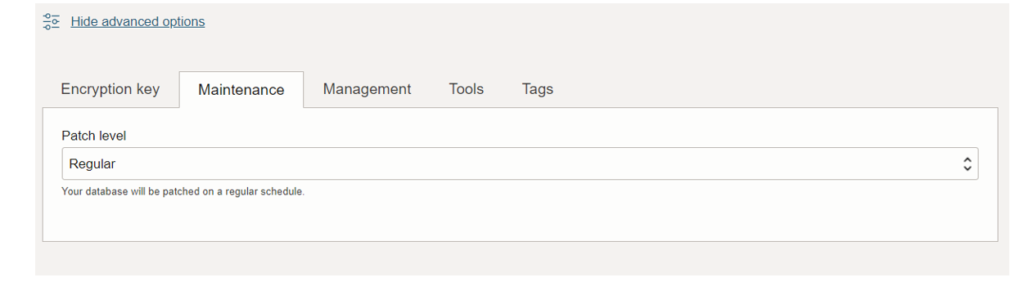
8. Maintenance. (Patch Level)
When we provision or clone an Autonomous Database instance, we can select a patch level to apply to upcoming patches. There are two patch-level options: Regular and Early.
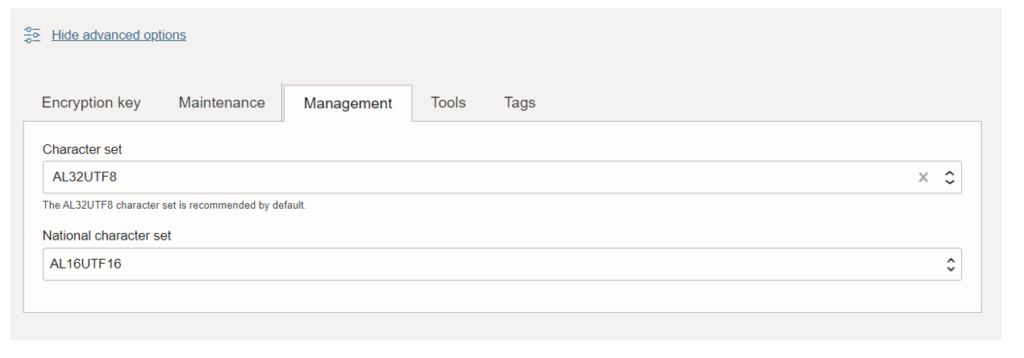
9. Management.
The Autonomous Database default database character set is Unicode AL32UTF8, and the default national character set is AL16UTF16.
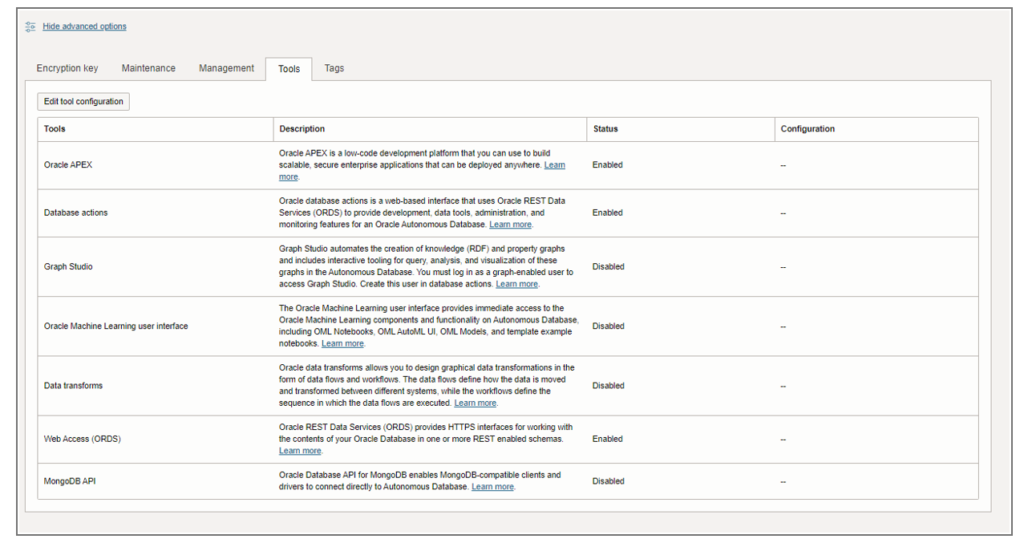
10. Tools.
Autonomous Database includes built-in tools that we can enable and disable when we provision or clone a database, or at any time for an existing database.
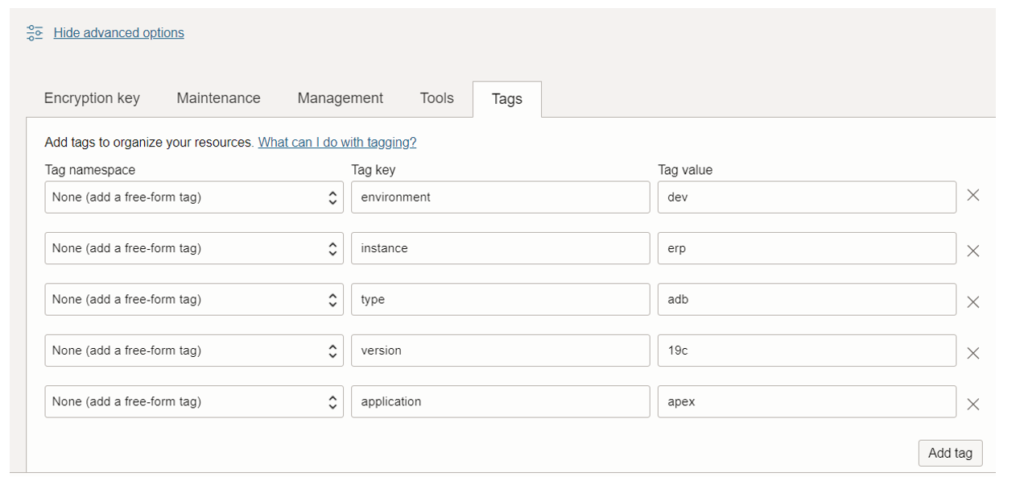
11. Tags
To apply, update, or remove defined tags for a resource, a user must be granted permissions on the resource and permission to use the tag namespace. Users must be granted use access to the tag namespace to apply, update, or remove a defined tag for a resource. When we create the tag key definition, you must choose the type of value (which also determines how the user applying the tag adds the value).
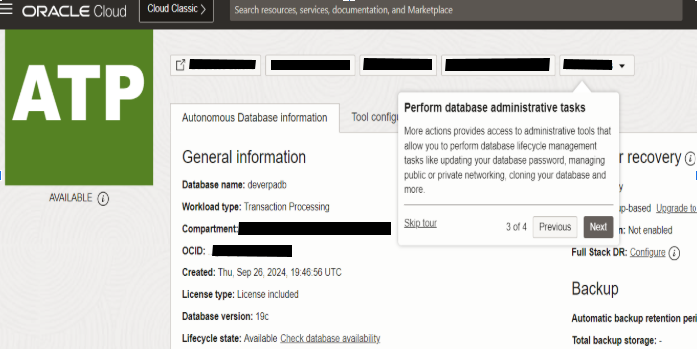
12. Autonomous Database Availability.
When the state filed is completed, the Lifecycle state changes from provisional to available.

 Abotts Partners with singapore based tech giant to help migrate their public sector customer from Sybase to SQL server.
Abotts Partners with singapore based tech giant to help migrate their public sector customer from Sybase to SQL server.
 Abotts partners with NYPL to integrate with their partner libraries.
Abotts partners with NYPL to integrate with their partner libraries.
 Upworks Inc partners with ABOTTS to build their Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) and migrate their custom applications to OCI.
Upworks Inc partners with ABOTTS to build their Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) and migrate their custom applications to OCI.
 Abotts Inc Partners with Gnorth consulting to deploy exadata and ODA for a large public sector customer.
Abotts Inc Partners with Gnorth consulting to deploy exadata and ODA for a large public sector customer.